|
Data Warehousing - For Better Business Decisions
Anjaneyulu Marempudi (marempudi@yahoo.com)
Introduction
In today’s competitive global business environment, understanding and managing
enterprisewide information is crucial for making timely decisions and responding to
changing business conditions. Many companies are realizing a business advantage by
leveraging one of their key assets - business data. There is a tremendous amount of data
generated by day-to-day business operational applications. In addition there is valuable
data available from external sources such as market research organizations, independent
surveys and quality testing labs. Studies indicate that the amount of data in a given
organization doubles every five years. Data Warehousing has emerged as an increasingly
popular and powerful concept of applying information technology to turn this huge islands
of data into meaningful information for better business decisions. Meta Group, Inc., a
leading consultant in the data warehousing environment, suggests that over 90% of the
Fortune 2000 businesses will put into place a data warehouse by the end of 1996.
What is Data Warehousing?
According to Bill Inmon, known as the father of Data Warehousing, a data warehouse is a
subject oriented, integrated, time-variant, nonvolatile collection of data in support of
management decisions.
- Subject-oriented
means that all relevant data about a subject is gathered and stored
as a single set in a useful format;
- Integrated
refers to data being stored in a globally accepted fashion with
consistent naming conventions, measurements, encoding structures, and physical attributes,
even when the underlying operational systems store the data differently;
- Non-volatile
means the data warehouse is read-only: data is loaded into the data
warehouse and accessed there;
- Time-variant data
represents long-term data--from five to ten years as opposed to
the 30 to 60 days time periods of operational data.
Data warehousing is a concept. It is a set of hardware and software components that can
be used to better analyze the massive amounts of data that companies are accumulating to
make better business decisions. Data Warehousing is not just data in the data warehouse,
but also the architecture and tools to collect, query, analyze and present information.
Data warehousing concepts
Operational / informational data:
Operational data is the data you use to run your business. This data is what is
typically stored, retrieved, and updated by your Online Transactional Processing (OLTP)
system. An OLTP system may be, for example, a reservations system, an accounting
application, or an order entry application.
Informational data is created from the wealth of operational data that exists in your
business and some external data useful to analyze your business. Informational data is
what makes up a data warehouse. Informational data is typically:
- Summarized operational data
- De-normalized and replicated data
- Infrequently updated from the operational systems
- Optimized for decision support applications
- Possibly "read only" (no updates allowed)
- Stored on separate systems to lessen impact on operational systems
OLAP / Multi-dimensional analysis:
Relational databases store data in a two dimensional format: tables of data represented
by rows and columns. Multi-dimensional analysis solutions, commonly referred to as On-Line
Analytical Processing (OLAP) solutions, offer an extension to the relational model to
provide a multi-dimensional view of the data. For example, in multi-dimensional analysis,
data entities such as products, geographies, time periods, store locations, promotions and
sales channels may all represent different dimensions. Multi-dimensional solutions provide
the ability to:
- analyze potentially large amounts of data with very fast response times
- "slice and dice" through the data, and drill down or roll up through various
dimensions as defined by the data structure
- quickly identify trends or problem areas that would otherwise be missed
Multi-dimensional data structures can be implemented with multidimensional databases or
extended RDBMSs. Relational databases can support this structure through specific database
designs (schema), such as "star-schema", intended for multi-dimensional analysis
and highly indexed or summarized designs. These structures are sometimes referred to as
relational OLAP (ROLAP)-based structures.
Data Marts:
Data marts are workgroup or departmental warehouses, which are small in size, typically
10-50GB. The data mart contains informational data that is departmentalized, tailored to
the needs of the specific departmental work group. Data marts are less expensive and take
less time for implementation with quick ROI. They are scaleable to full data warehouses
and at times are summarized subsets of more detailed, pre-existing data warehouses.
Metadata/Information Catalogue:
Metadata describes the data that is contained in the data warehouse (e.g. Data elements
and business-oriented description) as well as the source of that data and the
transformations or derivations that may have been performed to create the data element.
Data Mining:
Data mining predict future trends and behaviors, allowing businesses to make proactive,
knowledge driven decisions. Data mining is the process of analyzing business data in the
data warehouse to find unknown patterns or rules of information that you can use to tailor
business operations. For instance, data mining can find patterns in your data to answer
questions like:
- what item purchased in a given transaction triggers the purchase of additional related
items?
- how do purchasing patterns change with store location?
- what items tend to be purchased using credit cards, cash, or check?
- how would the typical customer likely to purchase these items be described?
- did the same customer purchase related items at another time?
Data Warehouse Implementation
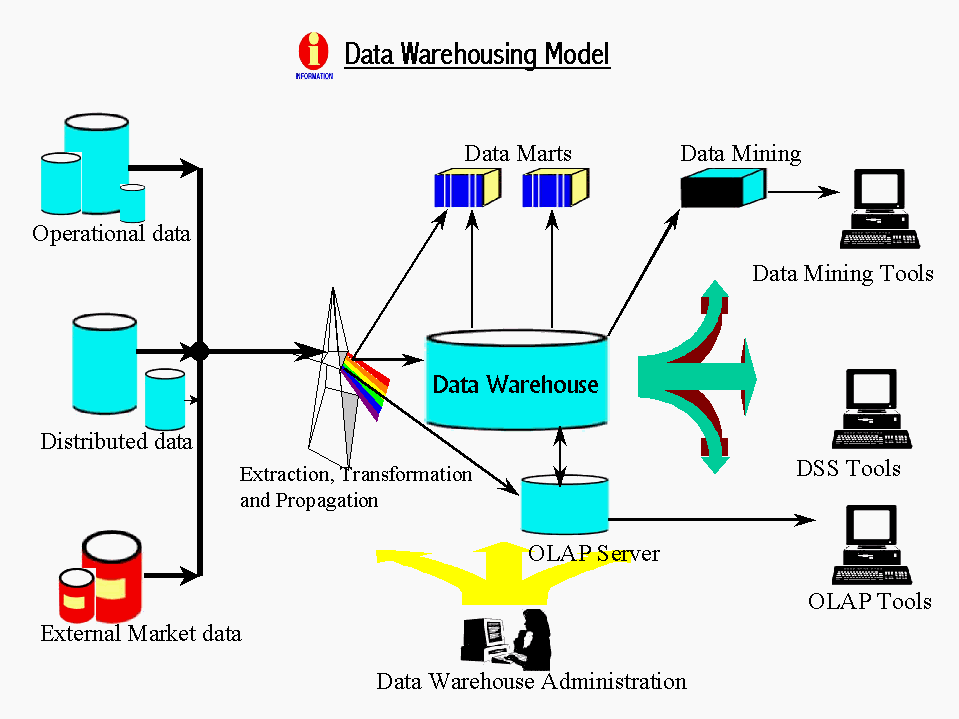
Fig 1: Data Warehousing Architecture Model
The following components should be considered for a successful implementation of a Data
Warehousing solution:
- Open Data Warehousing architecture with common interfaces for product integration
- Data Modeling with ability to model star-schema and multi-dimemsionality
- Extraction and Transformation/propagation tools to load the data warehouse
- Data warehouse database server
- Analysis/end-user tools: OLAP/multidimensional analysis, Report and query
- Tools to manage information about the warehouse (Metadata)
- Tools to manage the Data Warehouse environment
Transforming operational data into informational data:
Creating the informational data, that is, the data warehouse, from the operational
systems is a key part of the overall data warehousing solution. Building the informational
database is done with the use of transformation or propagation tools. These tools not only
move the data from multiple operational systems, but often manipulate the data into a more
appropriate format for the warehouse. This could mean:
- The creation of new fields that are derived from existing operational data
- Summarizing data to the most appropriate level needed for analysis
- Denormalizing the data for performance purposes
- Cleansing of the data to ensure that integrity is preserved.
Even with the use of automated tools, however, the time and costs required for data
conversion are often significant. Bill Inmon has estimated 80% of the time required to
build a data warehouse is typically consumed in the conversion process.
Data warehouse database servers--the heart of the warehouse:
Once ready, data is loaded into a relational database management system (RDBMS) which
acts as the data warehouse. Some of the requirements of database servers for data
warehousing include: Performance, Capacity, Scalability, Open interfaces, Multiple-data
structures, optimizer to support for star-schema, and Bitmapped indexing . Some of the
popular data stores for data warehousing are relational databases like Oracle, DB2,
Informix or specialized Data Warehouse databases like RedBrick, SAS.
To provide the level of performance needed for a data warehouse, an RDBMS should
provide capabilities for parallel processing - Symmetric Multiprocessor (SMP) or Massively
Parallel Processor (MPP) machines, near-linear scalability, data partitioning, and system
administration.
Data Warehousing Solutions - what is hot?
| Solution Area |
Product |
Vendor |
| Report and Query |
Impromptu
BrioQuery
Business Objects
Crystel Reports |
Cognos Brio Technology
Business Objects Inc
Seagate Software |
| OLAP / MD analysis |
DSS Agent/Server DecisionSuite
EssBase
Express Server
PowerPlay
Brio Enterprise
Business Objects |
Microstrategy Information
Advantage
Hyperion Solutions
Oracle Corp.
Cognos Corporation
Brio Technology
Business Objects |
| Data mining |
Discovery Server Intelligent
Minor
Darwin |
Pilot Software IBM
Thinking Machines |
| Data Modeling |
ER/Win |
Platinum |
| Data extraction,
transformation, load |
DataPropagator InfoPump
Integrity Data Re-Eng.
Warehouse Manager
PowerMart |
IBM Platinum Technology
Vality Technology
Prism Solutions
Informatica |
| Databases for data
warehousing |
DB2 Oracle Server
MS SQL Server
RedBrick Warehouse
SAS System
Teradata DBS |
IBM Oracle
Microsoft
Red Brick Corp.
SAS Institute
NCR |
| Information catalogue |
DataGuide HP Intelligent
Warehouse: Guide
Directory Manager |
IBM Hewlett-Packard
Prism Solutions |
Benefits of Data Warehousing
A well designed and implemented data warehouse can be used to:
- Understand business trends and make better forecasting decisions
- Bring better products to market in a more timely manner
- Analyze daily sales information and make quick decisions that can significantly affect
your company's performance
Data warehousing can be a key differentiator in many different industries. At present,
some of the most popular Data warehouse applications include:
- sales and marketing analysis across all industries
- inventory turn and product tracking in manufacturing
- category management, vendor analysis, and marketing program effectiveness analysis in
retail
- profitable lane or driver risk analysis in transportation
- profitability analysis or risk assessment in banking
- claims analysis or fraud detection in insurance
Conclusion
Data Warehousing provides the means to change raw data into information for making
effective business decisions--the emphasis on information, not data. The data warehouse is
the hub for decision support data. A good data warehouse will... provide the RIGHT data...
to the RIGHT people... at the RIGHT time: RIGHT NOW! While data warehouse organizes data
for business analysis, Internet has emerged as the standard for information sharing. So
the future of data warehousing lies in their accessibility from the Internet. Successful
implementation of a data warehouse requires a high-performance, scaleable combination of
hardware and software which can integrate easily with existing systems, so customers can
use data warehouses to improve their decision-making--and their competitive advantage.
|